Post Mortem: Kame Aggregator Exploit September 2025
1. Incident Summary
Overview: On September 12, 2025, certain Kame Aggregator experienced an exploit (“Exploit”) initiated by a primary exploiter (“Primary Exploiter”), leading to unauthorized extraction of a significant amount of assets of Kame users (“Affected Users”).
Response and Mitigation: As of confirmation, we immediately inform all users to take actions (revoke infinite permissions for our contracts), working with Sei Foundation and other related partners to cover all channels to Sei users. Since our contract doesn’t have PAUSE/UPGRADE functionality so it could only be done from users only. We contacted several security teams who could help us to notice partners like CEX, Circle, bridges to help us track down the exploiters. We also put bounties for some well-known security teams to track down the exploiters. And, we made contact with Primary Exploiter via onchain messages and successfully got Primary Exploiter to return part of lost funds.
Technical Vulnerability: The attacker leveraged a design flaw in the swap() function that allowed arbitrary executor calls, resulting in the theft of approximately [X USD worth of tokens] from users who had granted unlimited approvals.
Key Incident Metrics
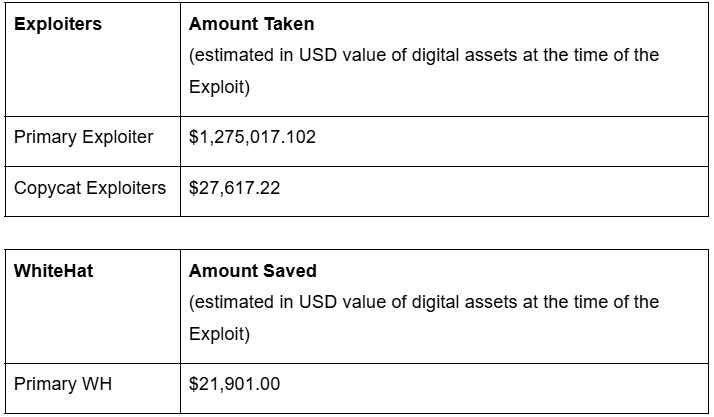
Affected Users: 830 unique users were impacted
Total Value of Affected Assets: Approximately $1,324,535.32 being the value of Affected Assets (Estimated in USD value of digital assets at the time of the Exploit)
Total Value of Affected Assets recovered by Kame Team from Primary Exploiter: Approximately $946,195.94
Total Value Recovered by White Hat Hackers::
Approximately $21,900.98
2. Technical Analysis:
Root Cause
The swap() function allowed arbitrary execution of params.executor with params.executeParams: (bool success, bytes memory returnData) = params.executor.call{value: msg.value}(params.executeParams);
No validation was performed on either the executor or the calldata. By setting the executor to a malicious Multicall contract 0xcA11bde05977b3631167028862bE2a173976CA11, the attacker could directly invoke a token’s transferFrom() against victims who had approved the router. This effectively turned the router into a proxy for token theft.
The impact was critical because many users had either granted unlimited allowances to the AggregationRouter or approved amounts larger than their intended swap sizes, leaving residual approvals exploitable.
Attack Flow
Exploit transaction (example): 0x1bf7a70c0f55344d3466fbce42317fbc842c29a25d1ed86253a2cc64163dfdc2
SrcToken: 0xE30f…e8C7
DstToken: 0xE30f…e8C7
Amount: 0
Executor: 0xcA11…CA11 (Multicall contract used as executor)
ExecuteParams: Encoded calldata for transferFrom(...)
Resulting on-chain action
transferFrom(
victim: 0x17860B2320A9B43a9B7F4d16fe8e51F4Ccfd92B8,
recipient: 0x3A42B17f0D25de388BF0b08ffd860cdBDDdfB110, // attacker
amount: 1105960373927494381965723
)
Impact
Funds lost: ~ $1,324,535.324 USD
Tokens affected: Tokens approved to the AggregationRouter at 0x14bb9...3308dc4d80
Victims: All addresses that had granted unlimited or oversized approvals (i.e., approvals larger than the intended swap amounts)
Primary exploiter wallet: 0x3A42B17f0D25de388BF0b08ffd860cdBDDdfB110.
11 copycat exploiters
3. Exploiters/WhiteHat
Following with Primary Exploiter, these are copycat exploiter who attacked the same vulnerability of Kame at the same time.
4. Response and Mitigation Steps
Following the significant impact of the incident, we have initiated a robust set of response and mitigation measures to address immediate issues and prevent similar events in the future.
User Alerts: We disseminated alerts via X, Telegram, Discord and on the Kame website, as well as through these tweets:
Onchain Communications: We sent several messages to the Primary Exploiter, offering a 20% bug bounty (detail here & here) and Primary Exploiter responded and returned part of the lost funds.
5. Impact Assessment
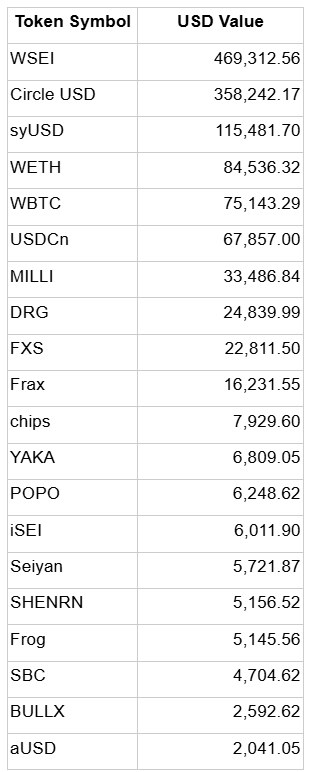
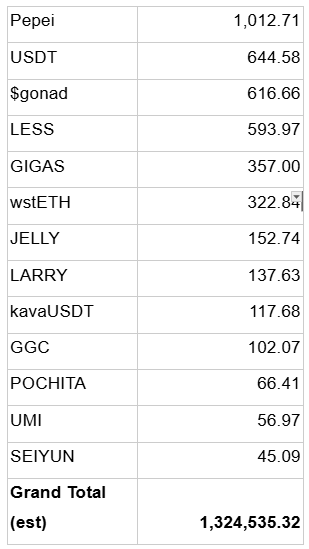
List of Affected Assets
Approximately $1,324,535.32 in value of Affected Assets was initially taken from the Affected Users by the Exploit. The following table summarizes the list of Affected Assets (price of Affected Assets is collected by the time of incident).
6. Compensation Plans
Kame team is working on our own for a compensation plan to all affected users.
Details will be shared immediately once the plan is ready.
7. Lesson Learned
Avoid arbitrary external calls: Arbitrary external calls in aggregation routers are inherently dangerous and must be avoided.
Strict executor whitelisting and validation: User approvals should always be paired with strict executor whitelisting and calldata validation.
Monitoring system: Continuous monitoring for abnormal transfer patterns can help detect and mitigate exploits earlier.
Enhance security Full audit and continuous checking for potential vulnerabilities that may arise.
Suspend/Upgrade ability Aggregator contract should be able to be suspended to prevent any further loss to protect users better.
Appendix
Vulnerable contract: 0x14bb98581ac1f1a43fd148db7d7d793308dc4d80
Exploit contract: 0xcA11bde05977b3631167028862bE2a173976CA11
Attacker wallet: 0x3A42B17f0D25de388BF0b08ffd860cdBDDdfB110
Example victim: 0x17860B2320A9B43a9B7F4d16fe8e51F4Ccfd92B8
Exploit transaction (example): 0x1bf7a70c0f55344d3466fbce42317fbc842c29a25d1ed86253a2cc64163dfdc2


With time this will all be history, Glad that the team has handled this well